Subcostal 4 chamber view showing hypertrophic LV with preserved LV function
Notice:
– Myocardial wall thickness is increased
– LV dimensions are often decreased
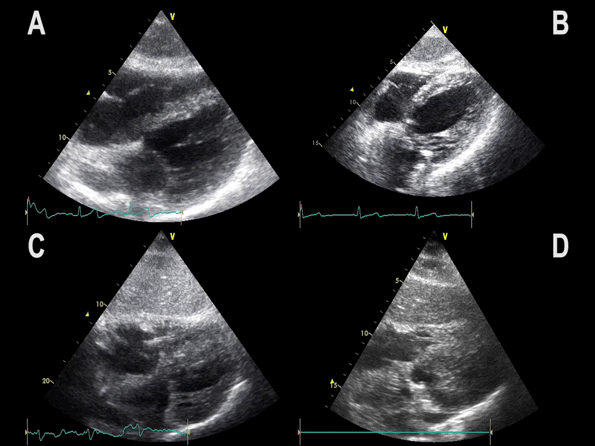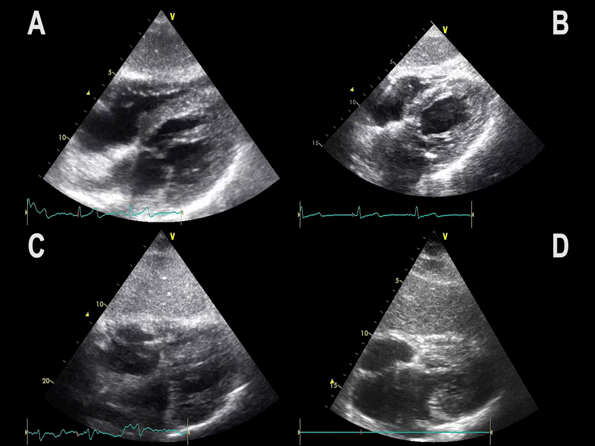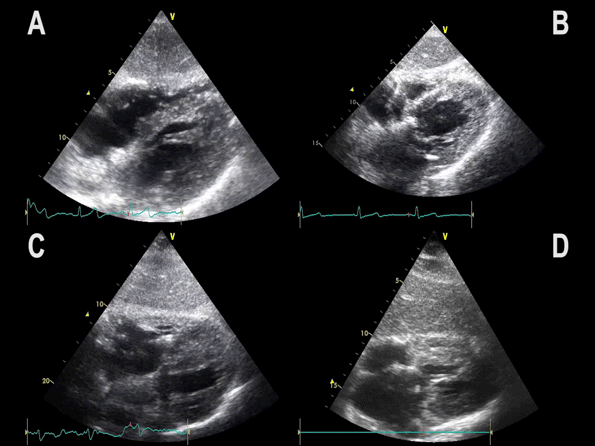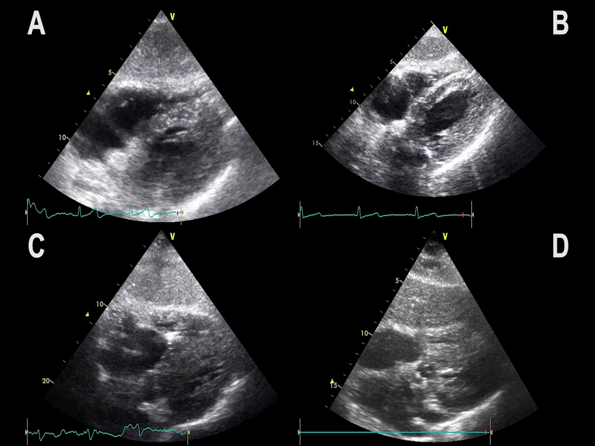
Subcostal 4 chamber view showing hypertrophic LV with preserved LV function
Notice:
– Myocardial wall thickness is increased
– LV dimensions are often decreased

Images and video clips of the parasternal short axis view
Notice:
– Reduced myocardial thickening
– Reduced endocardial movement
– Myocardial wall may appear thin

Images and video clips of the parasternal long axis view
Notice:
– LV is enlarged
– LA is enlarged
– Anterior mitral leaflet opening is compromised; MSS increased
– Myocardial wall may appear thin
– Reduced contractility

Images and video clips from the apical 4 chamber view
Notice:
– LV is enlarged
– LA is enlarged
– Anterior mitral leaflet opening is compromised; MSS increased
– Myocardial wall may appear thin
– Reduced contractility
– MAPSE is reduced

Images and video clips from the subcostal 4 chamber view
Notice:
– LV is enlarged
– LA is enlarged
– Anterior mitral leaflet opening is compromised; MSS increased
– Myocardial wall may appear thin
– Reduced contractility

Hypertrophic left ventricle
2D echocardiographic characteristics:
– Myocardial wall thickness is increased
– LV dimensions are decreased
– LA is often enlarged
– MAPSE is often slightly reduced

The FATE card page 3 provides the normal cardiac and pleural target images, as well as images of the most important cardiac pathologies and their presentation in the different FATE views
You can get the FATE card in the AppStore or Google Play

The following topics will focus on how to obtain and interpret the 2D ultrasound images for:
• Dilated, dysfunctional left ventricle
• Hypertrophic left ventricle with diastolic dysfunction
• Pericardial effusion / cardiac tamponade
• Dilated, dysfunctional right ventricle
• Pedunculated masses; endocarditis
• Pleural effusion
• Pulmonary edema
• Pneumothorax
• Aorta sclerosis
• Cardiac arrest
• Enlarged atrias
• IVC abnormalities

The 2D echocardiographic characteristics
Notice if:
– LV dimensions are increased
– Myocardial wall is thin
– Myocardial movement is reduced
– Mitral septal separation is increased
– Left atrium is often enlarged
– Mitral valve is incompetent
– Mitral annular plane systolic excursion (MAPSE) is reduced

The liver is used as the reference point when diaphragm and pleura on the patients right side are examined
The spleen is used as the reference point when diaphragm and pleura on the patients left side are examined
Evaluation of pleural effusion should always be performed with elevated thorax, as gravitation will affect the position of any pleural fluid
The diaphragm is a mandatory landmark – If you consider pleurocentesis, never insert a needle unless you have identified the diaphragm
