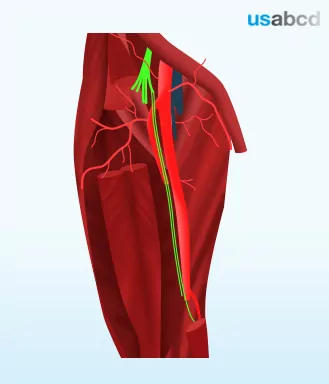
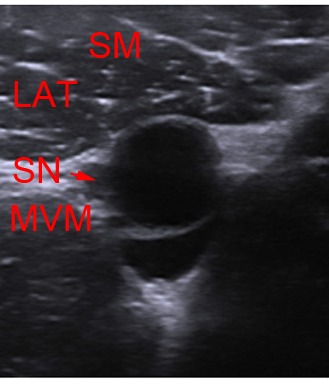
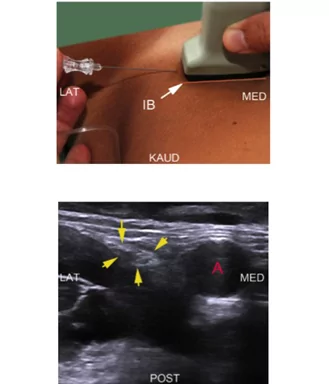
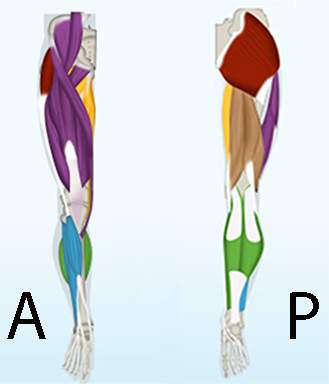
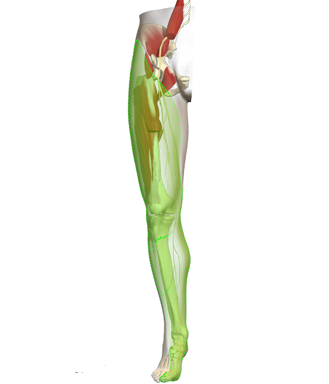
The saphenous nerve is the biggest branch from the femoral nerve
The saphenous nerve runs in the thigh in the femoral triangle and the adductor canal alongside the femoral vessels. In the femoral triangle and the upper part of the adductor canal the saphenous nerve is lateral to the vessels
The saphenous nerve is 100% sensitive innervating the medial part of the knee capsule, the skin and subcutaneous tissue antero-inferior to the knee, of the medial leg, the medial ankle joint and the subtalar joints
Indications: For surgical anaesthesia or pain management of the leg you should combine a sciatic and a saphenous nerve block