The thoracic paravertebral block was described the first time by Dr. Hugo Sellheim in 1905.

The thoracic paravertebral block was described the first time by Dr. Hugo Sellheim in 1905.

– pneumothorax (0.5%)
– sympathetic blockade with hypotension and bradycardia
– block failure 10%
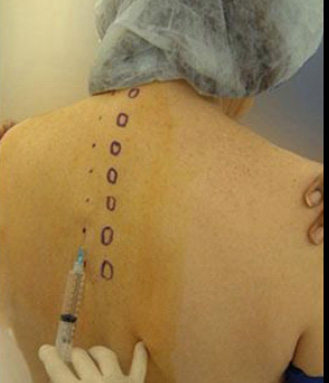
Absolute contraindications
– patient refusal
– allergy to local analgesics
– neoplasia in the thoracic paravertebral space
– empyema in the thoracic paravertebral space
– infection at the site of injection
Relative contraindications
– coagulopathy/anticoagulation
– ipsilateral diaphragmatic paresis
The learning objective of the expert ultrasound guided regional anaesthesia program is to obtain in-depth sonoanatomical theoretical knowledge about the selected expert nerve blocks.
Basic UGRA can be performed solely with a high-frequency linear probe.
Advanced and expert UGRA require high-frequency linear as well as low-frequency curved array probes.

Basic UGRA can be performed only with ultrasound without supplemental electrical nerve stimulation (ENS) technique.
Advanced and expert UGRA require a combination of ultrasound and ENS for various blocks.
ENS is obsolete for most blocks for the purpose of nerve localisation. However, sometimes peripheral nerves are not visible with ultrasound and ENS can be useful in order to confirm nerve identity.
Generally, the main purpose of ENS is a safeguard in order to assist avoiding accidental piercing of peripheral nerves and intraneural injection.
