Sauter A, Ullensvang K, Bendtsen TF, Børglum J: The “Shamrock Method” – a new and promising technique for ultrasound guided lumbar plexus block. http://bja.oxfordjournals.org/forum/topic/brjana_el%3b9814 (2013)
Sauter A, Ullensvang K, Bendtsen TF, Børglum J: The “Shamrock Method” – a new and promising technique for ultrasound guided lumbar plexus block. http://bja.oxfordjournals.org/forum/topic/brjana_el%3b9814 (2013)

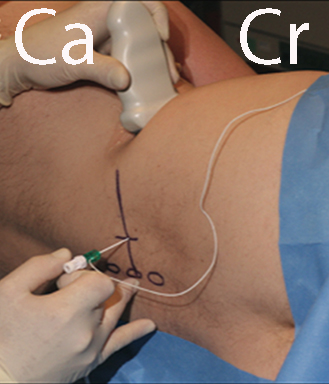
The ultrasound guided sacral plexus block – the socalled parasacral shift (PSPS) is indicated for:
– surgical anaesthesia of the hip combined with a lumbar plexus block
– postoperative analgesia after major hip surgery combined with a lumbar plexus block
– proximal sciatic blockade as an alternative to the subgluteal approach to block the sciatic nerve
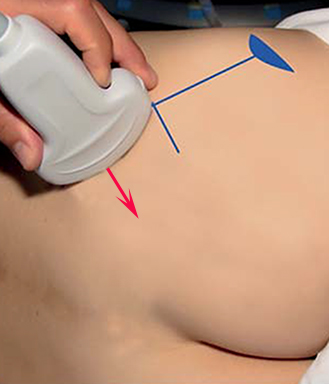
The parasacral region is covered by the gluteus maximus muscle
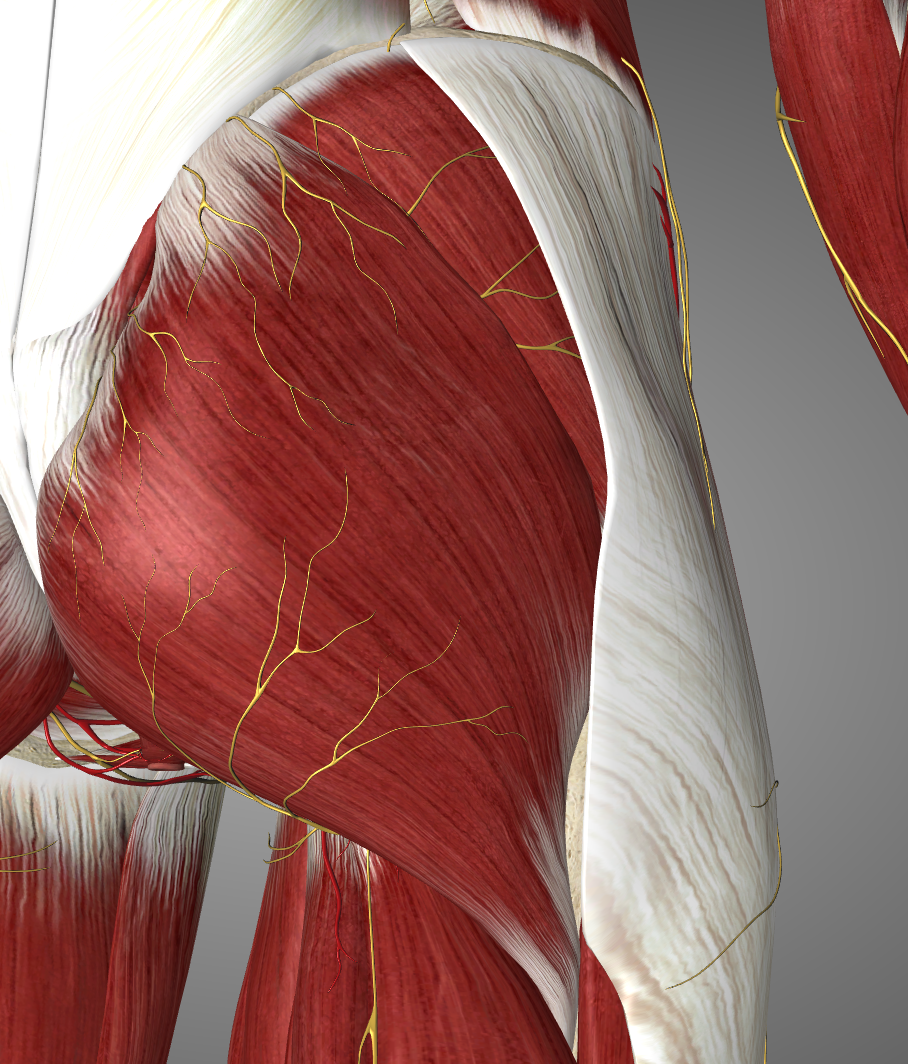
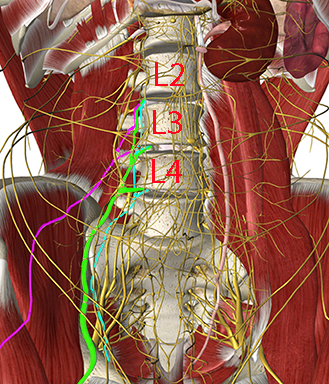
The important target nerves for the lumbar plexus block are the femoral nerve (L2-L4), the obturator nerve (L2-L4), and the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (L2-L3)
The other lumbar plexus nerves are not targeted with the lumbar plexus block, but are blocked selectively for some purposes (see other modules in this learning program): The iliohypogastric nerve (T12-L1), the ilioinguinal nerve (L1) and the genitofemoral nerve (L1-L2)
The femoral nerve innervates the iliopsoas, pectineus, sartorius, and quadriceps femoris muscles. It supplies sensory innervation to the hip joint, the anterior cutaneous branches of the thigh, the knee joint and via the saphenous nerve sensory branches to the knee region, the medial leg including branches to the medial ankle and subtalar joint capsules
The obturator nerve innervates the adductors (longus, brevis, magnus), gracilis, pectineus, and obturator externus
The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve supply sensory innervation to the lateral thigh
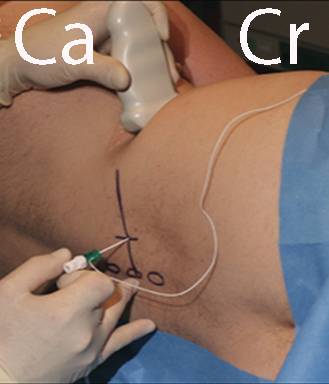
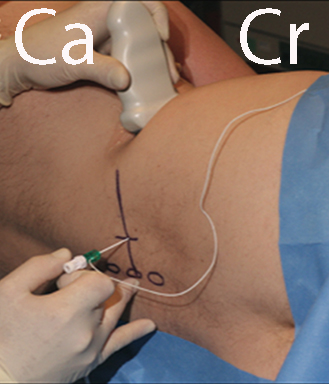
Place the patient in the lateral decubitus position
Place a low-frequency curved array probe in the axial plane in the flank just cranial to the iliac crest
The muscles of the abdominal wall are visualized (see next page). The probe is moved dorsal until the quadratus lumborum is seen medial to the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis
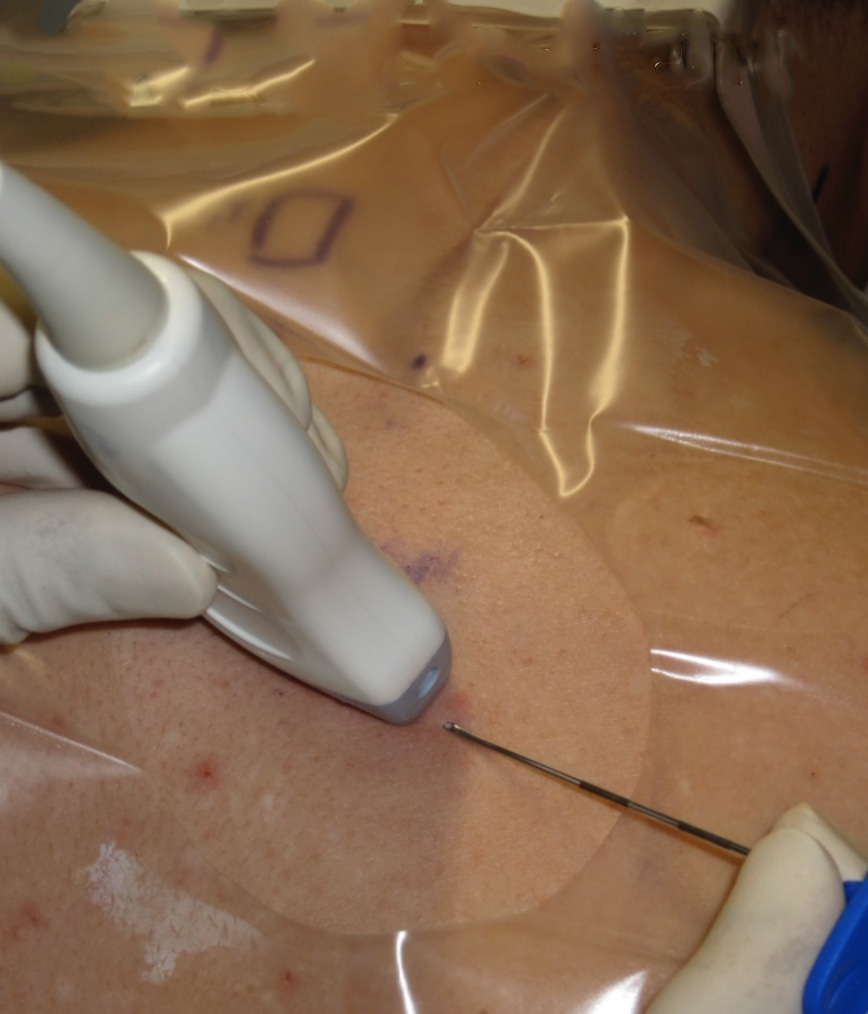
With a slight caudal tilt of the probe, the body and transverse process (TP) of vertebral body L4 can be seen surrounded by the “shamrock muscles” (see next page)
The lumbar plexus is visualized anterior to the TP (see second next page)
The needle is inserted from the back of the patient with in-plane technique and the needle tip is guided by ultrasound and electrical nerve stimulation to the target lumbar plexus (see third next page). Inject 20-30 mL of local anaesthetic.
The muscles of the abdominal wall (external and internal obliques and transversus abdominis) are visualized
The probe is moved dorsal until the quadratus lumborum is seen medial to the aponeurosis of the tranversus abdominis
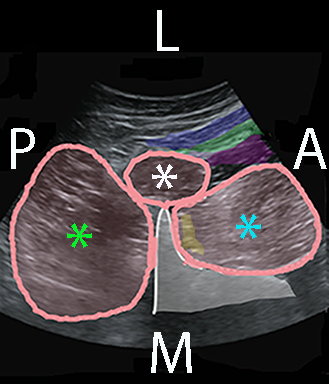
With a slight caudad tilt of the probe the body and transverse process (TP) of vertebral body L4 can be seen surrounded by the quadratus lumborum (QL) at the tip of the TP, erector spinae posterior to the TP and psoas major anterior to the TP
This is the “shamrock sign” – the treefoil of the stem of the TP surrounded by the three muscle “leaves”
The picture on the right is the same as on the previous page but without colour codes
Surgical anaesthesia for hip surgery in combination with a sacral plexus block as an alternative to general or spinal anaesthesia
Postoperative analgesia after major hip surgery
Combined analgesia of the femoral, obturator and lateral femoral cutaneous nerves
Technique 1:
– inject 15-20 mL of local anaesthetic at the midpoint of the desired level
– expect blockade of 4-5 dermatomes
Technique 2:
– extend blockade by 4-5 injections of 4-5 mL
Levels:
– simple mastectomy T3-T4
– open cholecystectomy T6-T7
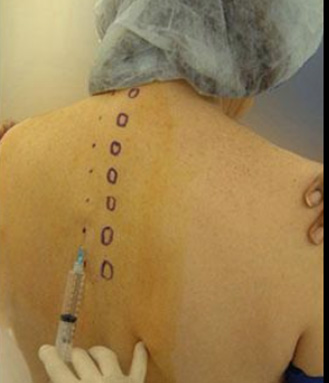
The needle is inserted with a lateral to medial in-plane approach