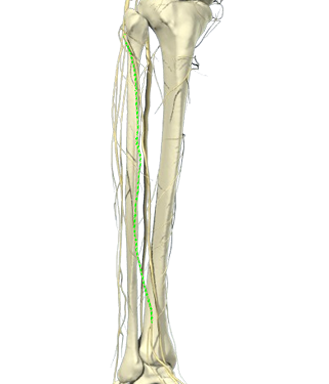
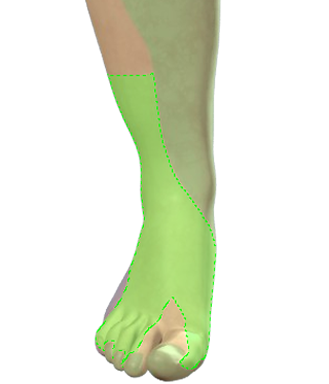
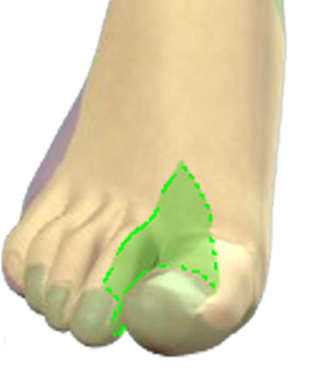
– Place the patient in the lateral position and the probe in the popliteal crease
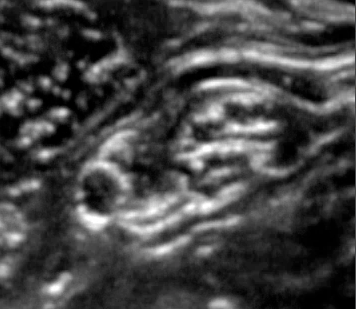
– Visualise the tibial nerve between the popliteal artery and the probe
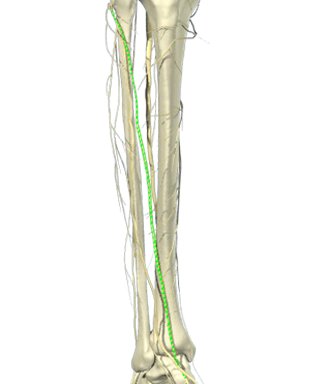
– Track the tibial nerve proximally until it unites with the peroneal nerve and the two become the sciatic nerve
– Insert the needle from the lateral end of the probe and advance the needle in-plane until the tip of the needle touches the peroneal nerve tangentially
– Inject the local anesthetic
– Relocate the tip of the needle until you obtain complete perineural spread of local anaesthetic around both the peroneal and the tibial nerve
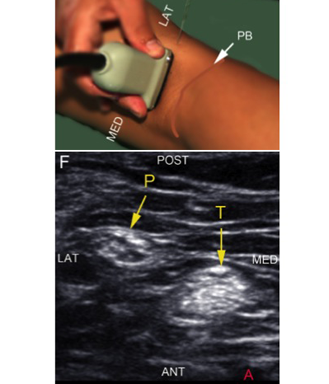
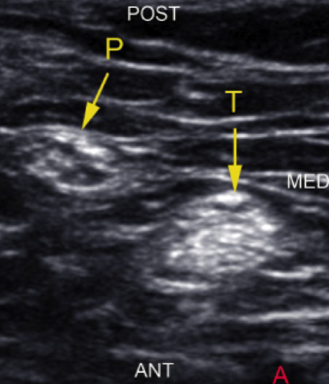
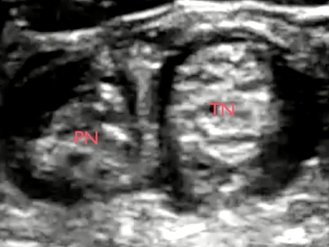
Bottom image: Sonoanatomy of the tibial and the peroneal nerve distal to the bifurcation of the sciatic nerve. (A) = popliteal artery; P = common peroneal nerve; T = tibial nerve; ant = anterior; post = posterior; lat = lateral; med = medial