The indications of the interscalene block are:
– Anaesthesia for shoulder surgery & shoulder
procedures
– Analgesia after shoulder surgery & shoulder
procedures
The ultrasound guided interscalene brachial plexus block is a basic level block
The indications of the interscalene block are:
– Anaesthesia for shoulder surgery & shoulder
procedures
– Analgesia after shoulder surgery & shoulder
procedures
The ultrasound guided interscalene brachial plexus block is a basic level block

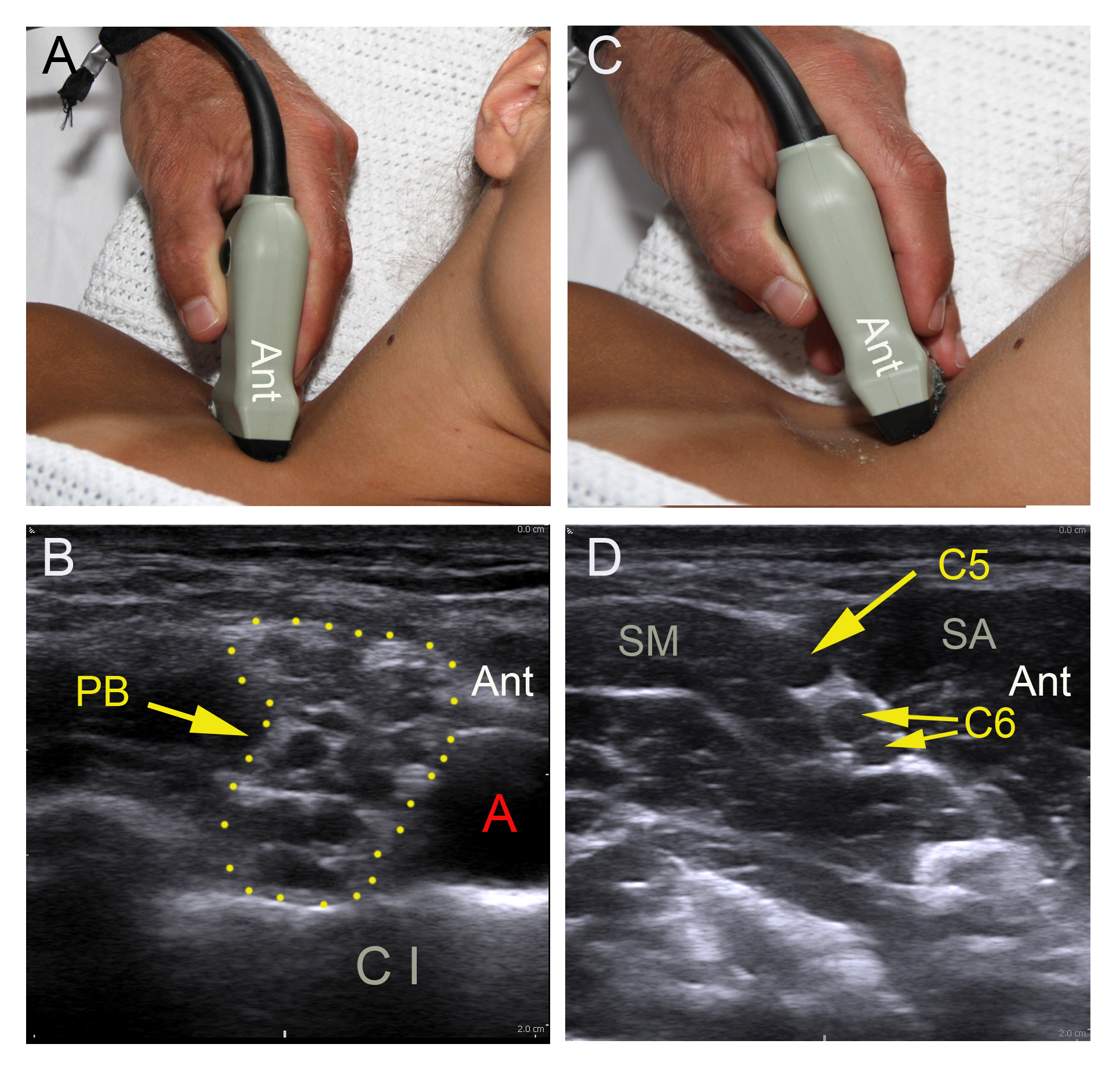
– Select a high-frequency linear probe
– Adjust gain, focus, and depth 2-3 cm
– Turn the orientation mark on the probe postero-lateral on the right side and antero-lateral on
the left side of the patient
– Place the probe behind the clavicle on top of the first rib oriented practically in the
parasagittal plane
– Locate the black, pulsatile subclavian artery (SA) on top of the first rib between the anterior
and the middle scalene muscles
– Locate the branches of the brachial plexus (BP) posterior to the SA
– Track the BP branches proximally until the profiles of the C5 and C6 spinal nerve roots line
up like a string of black pearls in the interscalene groove. C5 appears as one profile, C6 as
two
– Capture the best possible cross sectional image by tilting the probe and fine-tuning gain,
focus, and depth
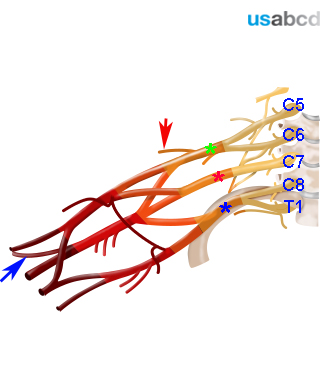
The brachial plexus (BP) innervates the upper limb
The BP originates from five spinal nerve roots: C5 to T1
The shoulder is innervated by the suprascapular nerve and the axillary nerve. They both originate from the spinal nerve roots C5 and C6
Anaesthesia of the shoulder requires blockade of the BP proximal to the level of the trunks, because the suprascapular nerve branches off the superior trunk
The shoulder and the shoulder joint is innervated by the axillary nerve and the suprascapular nerve
Minor contributions from the long thoracic nerve and capsular filaments from the infraspinatus nerve are not clinically significant