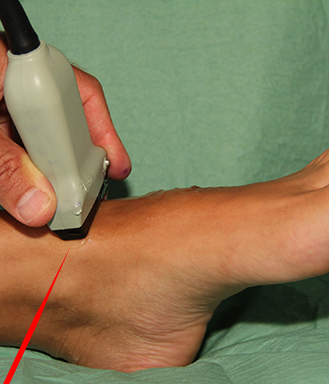
The sural nerve can be blocked as part of the ankle block with ultrasound guidance posterior to the lateral malleolus adjacent to the short saphenous vein
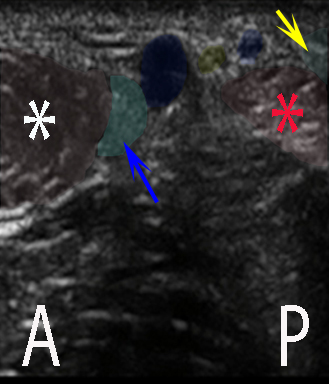
The sural nerve can be blocked as part of the ankle block with ultrasound guidance posterior to the lateral malleolus adjacent to the short saphenous vein

The saphenous nerve is usually not visible sonographically at the level of the ankle
It can be blocked by infiltrating the subcutaneous tissue around the long saphenous vein anterior to the medial malleolus
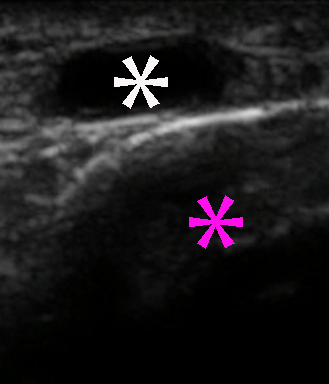
Fredrickson MJ: Ultrasound-guided ankle block. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 37(1): 143-44 (2009)
Lopez AM, Sala-Blanch X, Magaldi M, Poggio D, Asuncion J, Franco CD: Ultrasound-guided ankle block for forefoot surgery: The contribution of the saphenous nerve. Reg Anesth Pain Med 37(5): 554-57 (2012)
Coe A, Ram S: Ultrasound-guided ankle block for forefoot surgery: Is sural nerve block necessary? Reg Anesth Pain Med 38(3): 251 (2013)
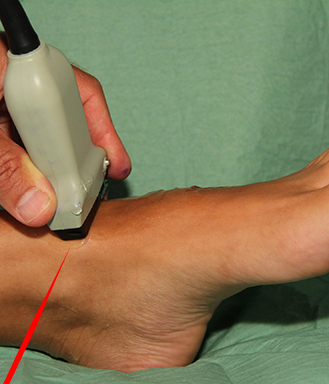
The deep peroneal nerve can be blocked with ultrasound guidance 5-10 cm proximal to the ankel, where the target runs adjacent to the anterior tibial artery sandwiched between the muscles of the anterior compartment and the interosseous membrane
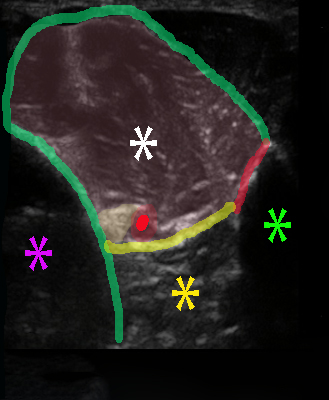
The superficial peroneal nerve is most suitably visualized and blocked approx. 10 cm proximal to the lateral malleolus where the target nerve emerges between the anterior and lateral compartments
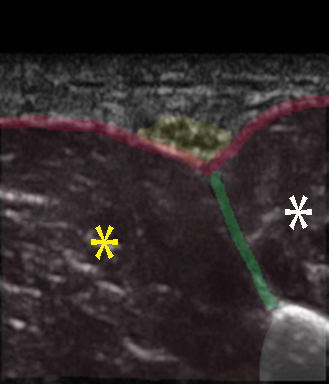
For an ankle block, the tibial nerve can be blocked with ultrasound guidance posterior to the medial malleolus, where the target nerve descends together with the posterior tibial artery and vein
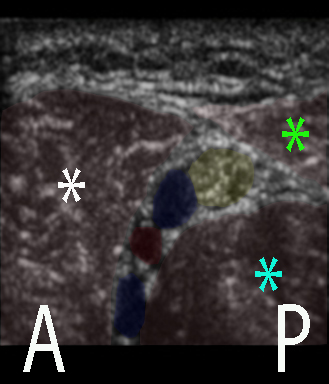
The deep peroneal nerve (DPN) branches off the common peroneal nerve in the proximal part of the lateral compartment
The DPN pierces the anterior intermuscular septum – that separates the lateral and the anterior/extensor compartments of the leg – and descends sandwiched between the interosseous membrane and the extensor muscles of the anterior compartment
The DPN innervates the extensor muscles of the anterior compartment (tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus & brevis, extensor hallucis longus & brevis and fibularis tertius)
The terminal cutaneous branch of the DPN runs deep the extensor retinacula anterior to the ankle together with the doral pedal artery and pierces the deep fascia on the distal part of the dorsum of the foot and supplies the lateral cutaneous nerve of the big toe and the medial cutaneous nerve of the second toe
The tibial nerve branches off the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa and descends in the midline in the deep part of the posterior compartment together with the posterior tibial artery and vein
It continues distally through the tarsal tunnel (below the flexor retinaculum between the calcaneus and the medial malleolus) behind the medial malleolus and supply cutaneous and muscular innervation via the medial and lateral plantar nerves to the plantar side of the foot and the sensory medial calcaneal branch to the medial side of the heel; it also supplies cutaneous innervation via the sural nerve
The tibial nerve innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg: triceps surae, plantaris, popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus
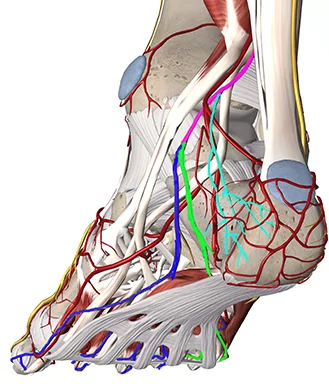
The saphenous nerve is the only nerve innervating the ankle and foot that is not a sciatic nerve branch – it is a purely sensory nerve
The saphenous nerve branches off the femoral nerve in the subinguinal region and descends subsartorially first in the femoral triangle and then into the adductor canal, where it pierces the vastoadductor membrane and emerges between the sartorius and gracilis and pierces the deep fascia on the medial side of the knee
A sensory infrapatellar branch supplies sensory branches to the medial part of the knee
The saphenous nerve supplies sensory branches to the medial side of the leg, ankle and foot including the medial part of the capsules of the ankle joint and the subtalar joints
On the medial side of the leg and ankle the saphenous nerve is joined by the long saphenous vein
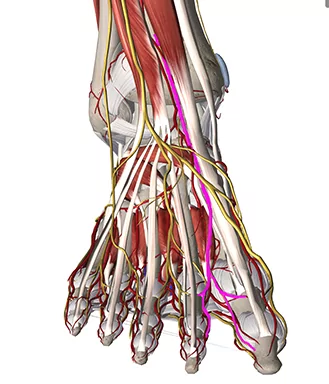
All five nerves innervating the ankle are blocked in an ankle block. Place the patient supine.
The probe is a high-frequency linear probe and all five nerves are scanned in short-axis view: – the deep peroneal nerve is blocked anterior to the ankle joint where it is adjacent to the dorsal pedis artery
– the superficial peroneal nerve is blocked approx. 10 cm proximal to the lateral malleolus where it emerges between the lateral and anterior compartments
– the tibial nerve is blocked posterior to the medial malleolus where it is adjacent to the posterior tibial artery
– the sural nerve is blocked posterior to the lateral malleolus where it is adjacent to the short saphenous vein
– the saphenous nerve is blocked anterior to the medial malleolus by infiltrating the subcutaneous tissue around the long saphenous vein
The target nerve and proxy arteries are visualized (see next pages) and the needle is inserted with in-plane technique. Inject approx. 3-4 mL perineurally around each target nerve