DVT
Introducción
La ecografía en el punto de atención puede determinar la presencia de trombosis venosa profunda (TVP) en la extremidad inferior de pacientes en situaciones críticas.
La evaluación de TVP puede ser útil para anestesiólogos, médicos de emergencias, intensivistas u otros médicos. La evaluación de TVP tiene utilidad en consultorios, departamentos de emergencia, evaluación preoperatoria, periodo postoperatorio o cuando los pacientes se encuentran en estado crítico.
Autores del programa de aprendizaje en línea:



Introduction
Point of care ultrasound can determine the presence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in the lower extremity of patients in critical situations.
DVT evaluation may be useful for anesthesiologists, emergency physicians, or intensivists, or other physicians. There is utility of DVT evaluation in clinics, emergency departments, preoperative evaluation, post-operative period, or when patients are in critical condition
Authors of the e-learning program:



Deep Venous Thrombosis Evaluation
The evaluation of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) shares the following characteristics with other point-of-care ultrasound applications:
• It is performed by clinicians treating the patient at the bedside or at the “point of care.”
• It answers a clear diagnostic question that guides clinical care and immediately improve patient outcomes.
• The exam is focused and goal directed, limited in scope, and answers a binary question.
• The findings are easy to recognize.
• The exam is easily learned and quickly performed.
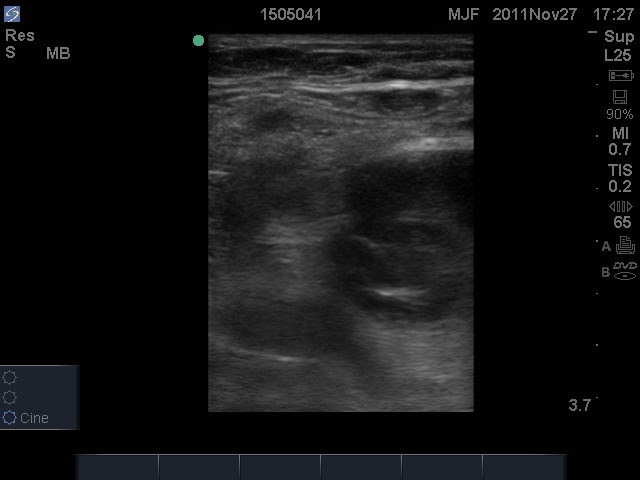
Point of Care Ultrasound (PoCUS) Diagnosis of Deep Venous Thrombosis
The evaluation of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) shares the following characteristics with other point-of-care ultrasound (PoCUS) applications:
• It is performed by clinicians treating the patient at the bedside or at the “point of care.”
• It answers a clear diagnostic question that guides clinical care and immediately improve patient outcomes.
• The exam is focused and goal directed, limited in scope, and answers a binary question.
• The findings are easy to recognize.
• The exam is easily learned and quickly performed.