FM-quiz LUSbas
FM-quiz LUSbas
Quiz Summary:
0 of 17 questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 17
Time has elapsed
0 of 0 point(s), (0)
0 of 0, (0)
Essay(s) Pending: 0 (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- FillInTheBlank 0%
- Multiple Choice 0%
- Summary 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
1 of 17Question1Correct OM and OI orientation and screen presentation, left side. Explore the image with regard to orientation marker (OM), orientation indicator (OI) and image presentation on the screen. Select the true statement below.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
2 of 17Question2Correct OM and OI orientation and screen presentation, right side. Explore the image with regard to orientation marker (OM), orientation indicator (OI) and image presentation on the screen. Select the true statement below.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
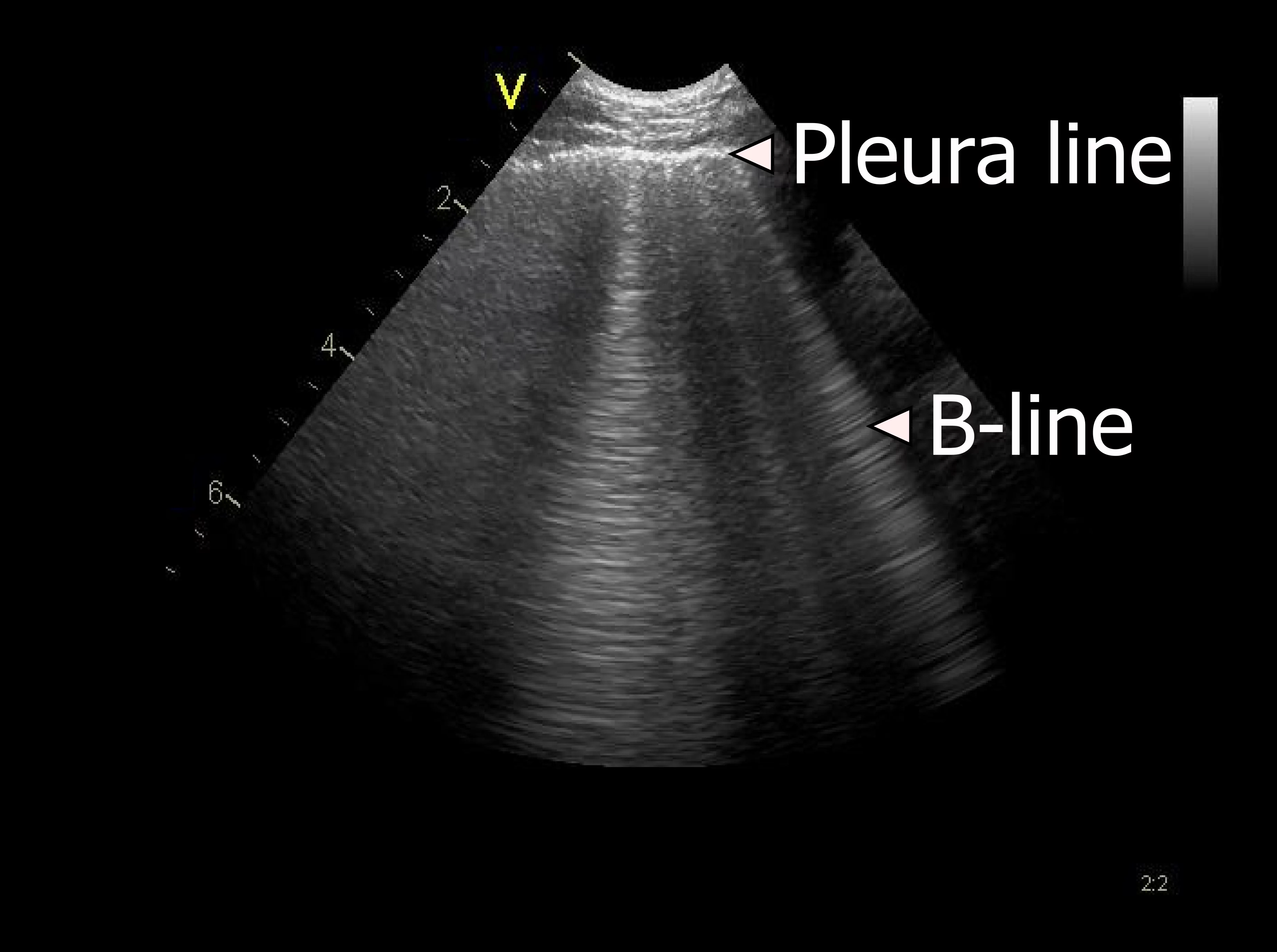
3 of 17Question3B-lines. Which of the following statements about B-lines are correct? Select all that apply.
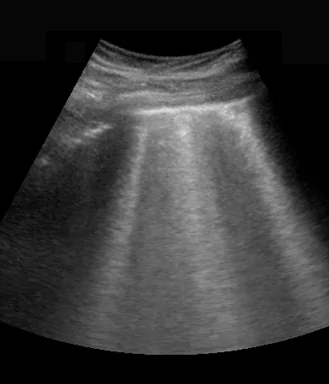 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
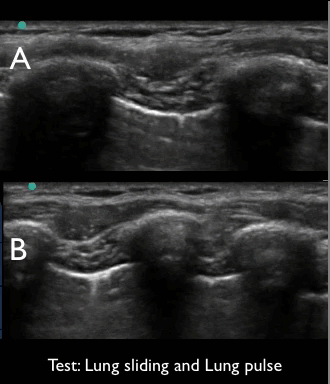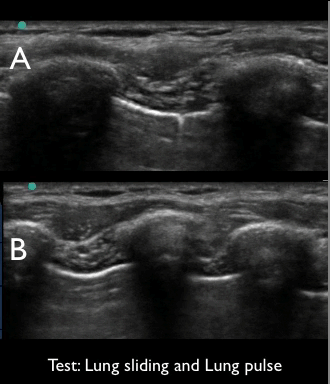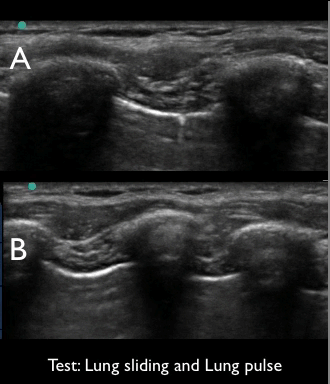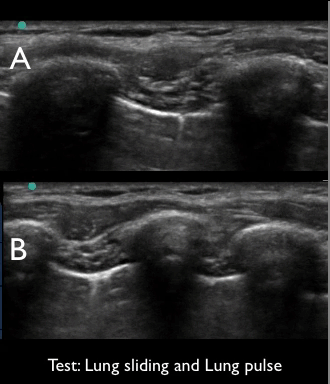
4 of 17Question4“Lung sliding” and “lung pulse”. Examine the video clips and select the true statement below.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
5 of 17Question5Identify the “sliding” sign. Which of the following statements are correct? Select all that apply.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
6 of 17Question6Lung point. Which of the following statements about lung point are correct? Select all that apply.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
7 of 17Question7Use of lung ultrasound signs in PTX. Which of the following statements about lung ultrasound signs are correct? Select all that apply.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
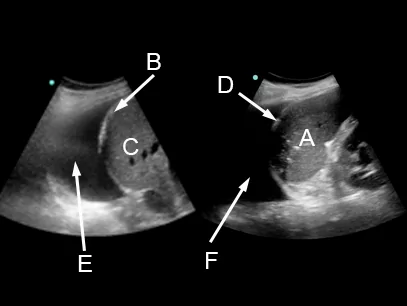
8 of 17Question8Causes of the interstitial syndrome. Examine the image and select which of the statements below are correct. Select all that apply.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
9 of 17Question9B-lines. Examine the video clip and select which of the statements below are correct. Select all that apply.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
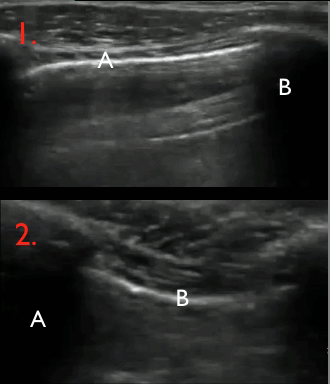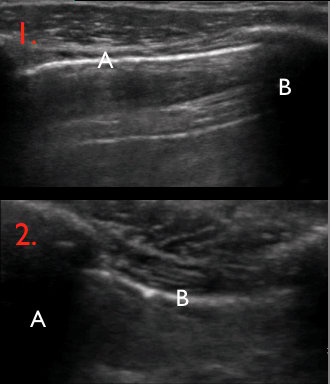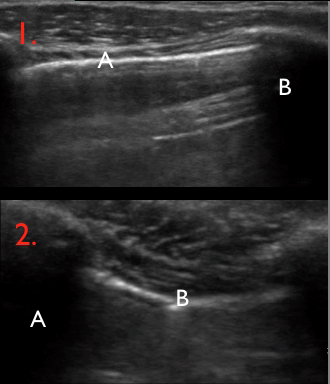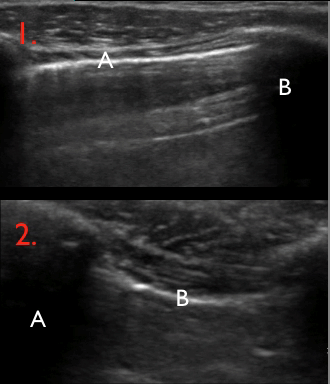
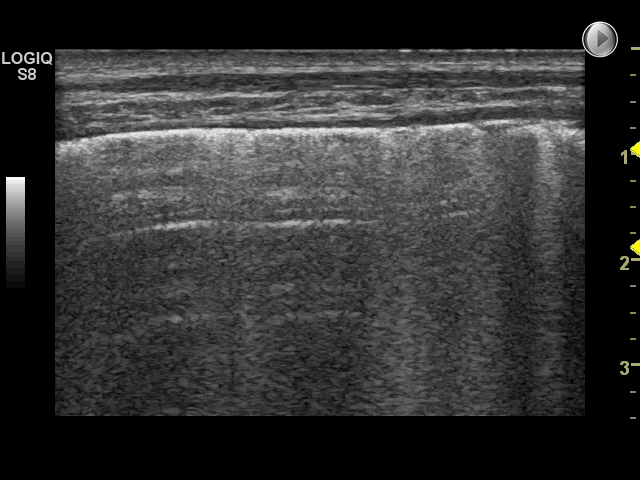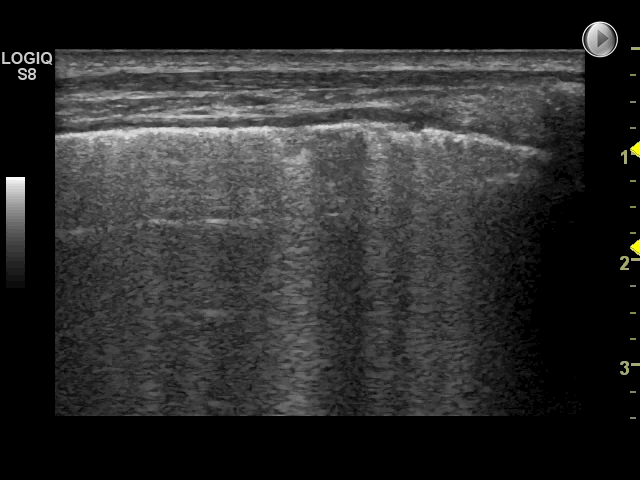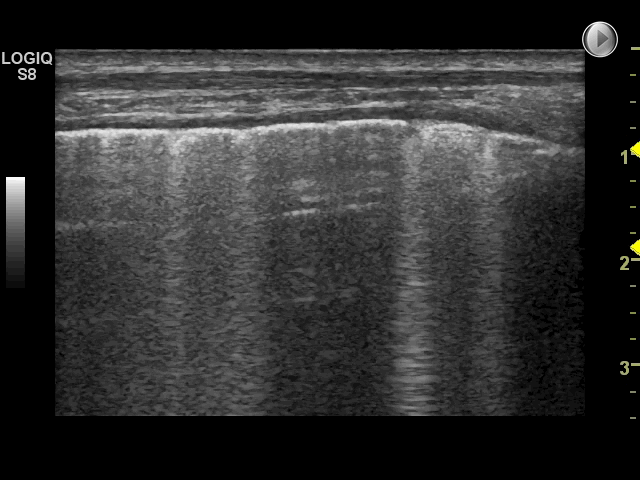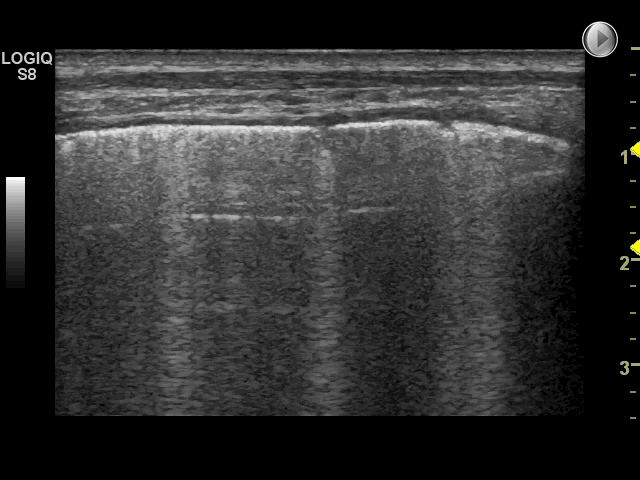
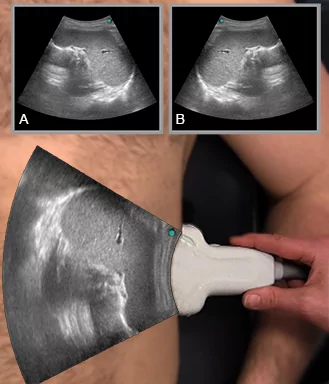
10 of 17Question10
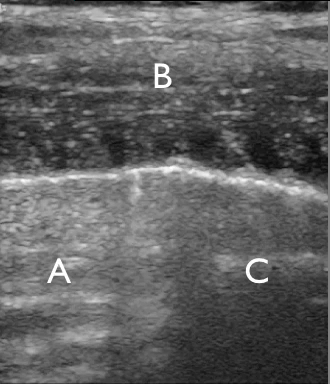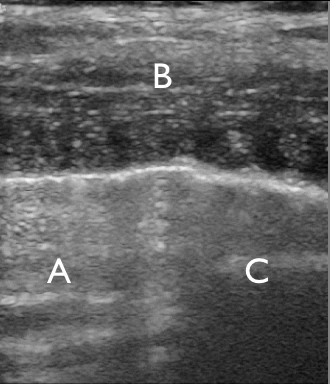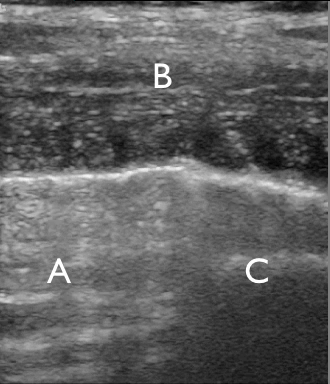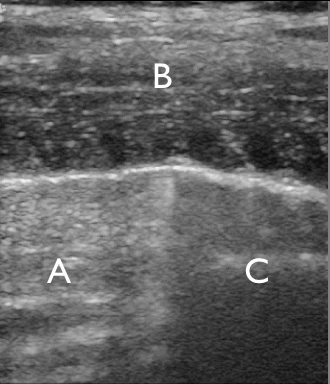
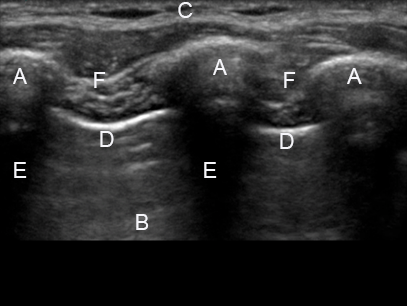
Identify the structures on the ultrasound image of the chest wall
In the image each letter labels a structure. Insert the correct letters for each statement and click “Next”.
-
shows image artefacts from the echoes of the overlying skin, muscle, costae and pleural lineshows skinshows intercostal muscleshows costashows pleurashows rib shadow
CorrectIncorrect -
-
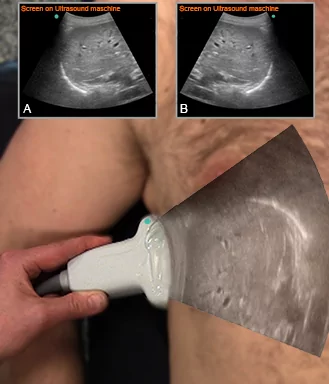
11 of 17Question11
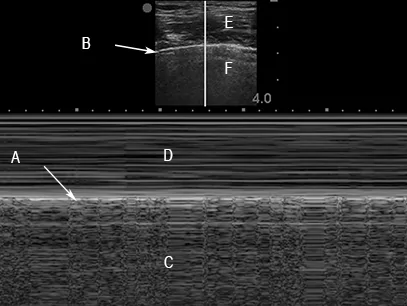
M-mode image of normal lung sliding
In the image each letter labels a structure. Insert the correct letters for each statement and click “Next”.
-
shows skin and subcutaneous tissue in real-time ultrasoundshows pleura in 2D real-time ultrasoundshows M-mode imaging of pleurashows lung artefact in 2D real-time ultrasoundshows “shore” in seashore signshows “sea” in seashore sign
CorrectIncorrect -
-
12 of 17Question12
Identify the structures
In the image each letter labels a structure. Insert the correct letters for each statement and click “Next”.
-
shows the diaphragm on the right sideshows the diaphragm on the left sideshows the livershows the area corresponding to right lungshows the area corresponding to left lungshows the spleen
CorrectIncorrect -
-
13 of 17Question13
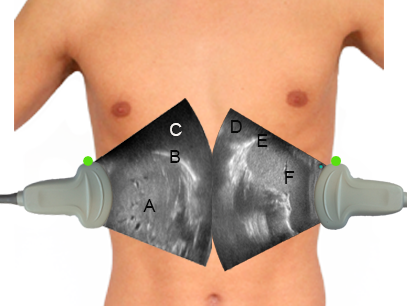
Identifying structures in pleural effusion
In the image each letter labels a structure. Insert the correct letters for each statement and click “Next”.
-
shows diaphragm on the left sideshows diaphragm on the right sideshows pleural effusion between left lung and left diaphragmshows pleural effusion between right lung and right diaphragmshows livershows spleen
CorrectIncorrect -
-
14 of 17Question14
Match the phrase at the top with the correct option below to form true statements by dragging the answer into the answer box.
Sort elements
- B-lines
- the liver is used as reference point
- a normal lung sign in M-mode ultrasound imaging
- lung pulse
- sliding of the visceral pleura against the parietal pleura with respiration
- the spleen is used as reference point
-
Hyperechoic, laser-like, vertical reverberation artefacts arising from the pleura line are called
-
In examination of the right pleura
-
Seashore sign is
-
When the pleural line is moving in synchrony with the cardiac pulsation it is called
-
The lung sliding sign is
-
In examination of the left pleura
CorrectIncorrect -
15 of 17Question15
Match the phrase at the top with the correct option below to form true statements by dragging the answer into the answer box.
Sort elements
- rules out PTX
- is an alternating seashore and stratosphere sign
- raises suspicion about PTX
- is the M-mode sign indicating PTX
- rules in/confirms PTX
- immediate needle decompression and emergency chest drainage is indicated without further diagnostics
-
Presence of either lung sliding, B-lines or lung-pulse
-
The M-mode presentation of the lung point
-
Absence of lung sliding, B-lines and lung pulse
-
The stratosphere sign
-
Absence of lung sliding, B-lines and lung-pulse, and presence of lung-point
-
In a critically ill patient with serious B- and/or C-problems and no lung sliding, B-lines and lung pulse
CorrectIncorrect -
16 of 17Question16
Match the phrase at the top with the correct option below to form true statements by dragging the answer into the answer box.
Sort elements
- anechoic area between the diaphragm and the lung
- pleural ultrasound should be performed to rule out the presence of pleural fluid
- is to identify the spleen
- while approx. 5 mL of pleural effusion can be detected with FLUS in the costophrenic recess in a sitting patient
- a pleural volume of approx. 400 mL can be expected
- confirms the absence of pleural effusion
-
Ultrasound detects pleural effusion as an
-
In all patients with oxygenation problems
-
First step in performing pleural ultrasound on the left side
-
CxR requires minimum 150 ml of pleural fluid for detection
-
When an anechoic brim of 20 mm is measured between parietal and visceral pleura in end-expiration
-
Presence of normal lung ultrasound signs in the phrenicocostal sinus during inspiration
CorrectIncorrect -
17 of 17Question17
Match the phrase at the top with the correct option below to form true statements by dragging the answer into the answer box.
Sort elements
- rules out cardiogenic pulmonary edema
- interstitial syndrome is absent
- as focal B-lines
- can be used to rule out PTX
- can be seen in ARDS
- may be a normal finding
-
Absence of the interstitial syndrome
-
In patients with isolated COPD exacerbation
-
Pneumonia can appear
-
The presence of B-line(s)
-
Presence of the interstitial syndrome
-
Focal B-lines
CorrectIncorrect